The Decline of Nuclear Disarmament
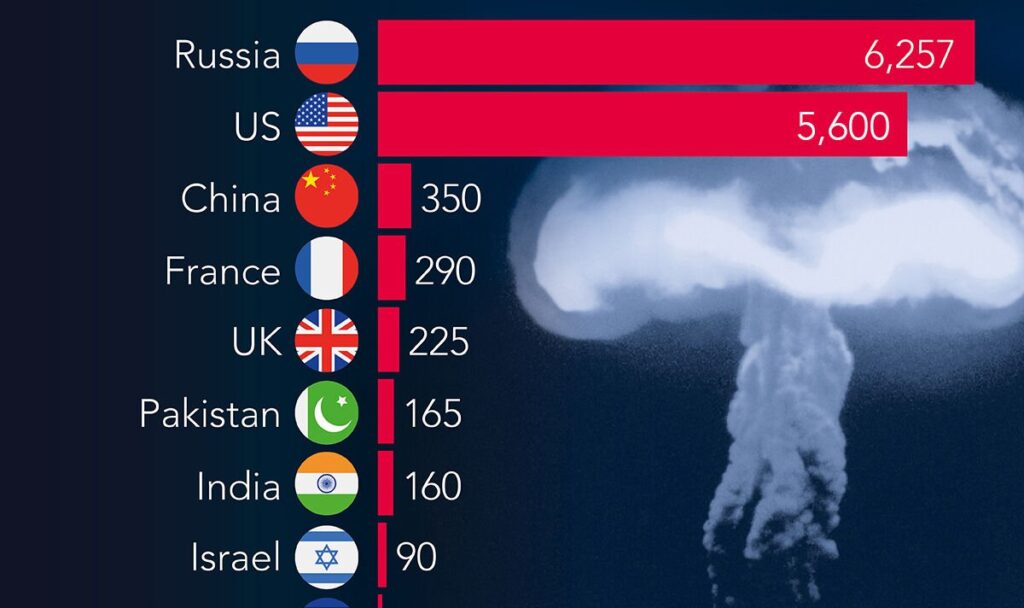
The worldwide motion towards Nuclear Arsenal seems to be dropping momentum, in accordance with latest findings by the Stockholm Worldwide Peace Analysis Institute (SIPRI). Amid rising geopolitical tensions and ongoing regional conflicts, SIPRI stories a slight improve within the variety of operational nuclear warheads over the previous yr. As of 2025, there are roughly 9,614 warheads prepared to be used—a rise of 0.3% in comparison with 2024—out of a complete stockpile of 12,241, which incorporates decommissioned weapons.
The institute warns that efforts towards disarmament are extra stalled than at any level for the reason that Chilly Struggle, particularly with the near-complete breakdown of strategic arms discussions between the USA and Russia.
China’s Accelerating Nuclear Enlargement
China is quickly increasing its nuclear capabilities, outpacing different nations in modernization and infrastructure growth. SIPRI notes that China has been developing new intercontinental ballistic missile (ICBM) silos throughout northern and central-eastern areas of the nation. Since 2023, its arsenal has grown by about 100 warheads yearly, reaching an estimated 600 by 2025. This development locations China third globally when it comes to nuclear stockpiles.
Regardless of this enlargement, most of China’s warheads should not but mounted on launch-ready techniques. Analysts recommend that by 2030, China may possess a comparable variety of ICBMs to both the U.S. or Russia, although its total arsenal will possible stay smaller. Diplomatic tensions, significantly regarding Taiwan and ongoing financial sanctions, have disrupted nuclear-related dialogue between Beijing and Washington.
U.S.-Russia Arms Management at Danger
Russia and the USA proceed to dominate the worldwide nuclear panorama, collectively holding practically 90% of all nuclear weapons. Each international locations are closely investing in modernizing their arsenals, elevating issues a few doable improve in deployed warheads as soon as the New START treaty expires in February 2026.
Whereas Russia has confronted challenges in its modernization packages—together with take a look at failures and delays with the Sarmat ICBM—different upgrades are transferring ahead slowly. In the meantime, the U.S. is underneath strain to answer China’s developments. Potential measures embody activating idle missile silos, increasing non-strategic nuclear forces, and deploying extra warheads to current supply techniques.
Nuclear Developments in Europe: France and the UK
France stays Europe’s main nuclear energy with a stockpile of round 290 operational warheads. The nation is advancing its nuclear capabilities by way of the event of latest submarine-launched ballistic missiles and air-launched cruise missiles.
Equally, the UK is enhancing its nuclear deterrent by way of maritime forces. Whereas its nuclear rely has remained steady at 225 warheads, the UK lately introduced important investments in as much as 12 new nuclear-powered submarines underneath the AUKUS protection pact. This enlargement is a part of a broader £15 billion (€17.5 billion) initiative geared toward strengthening its warhead infrastructure in response to evolving safety threats.




















 Animals
Animals